Tad Friend’s “Letter from California” articles in the New Yorker are probably the long-form journalism I most anticipate, in part because I’m fascinated from a distance with the opposite coast, but chiefly because he’s so good at understanding the micro and macro of any situation or subject and sorting through psychological motivations that drive the behavior of individuals or groups. To put it concisely: He gets ecosystems.
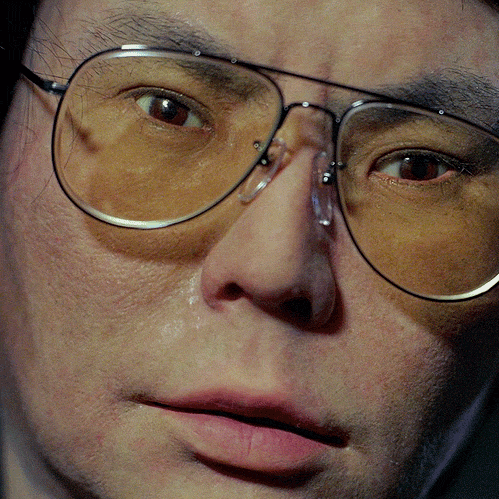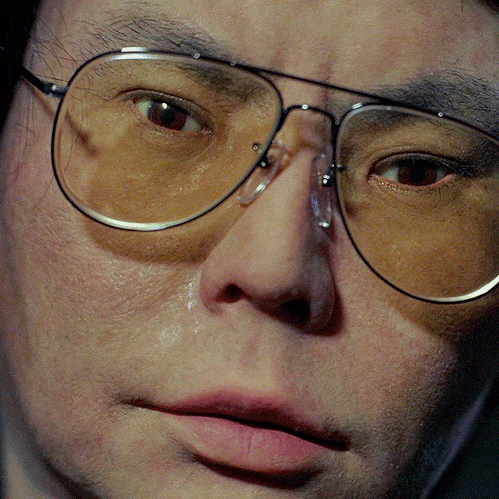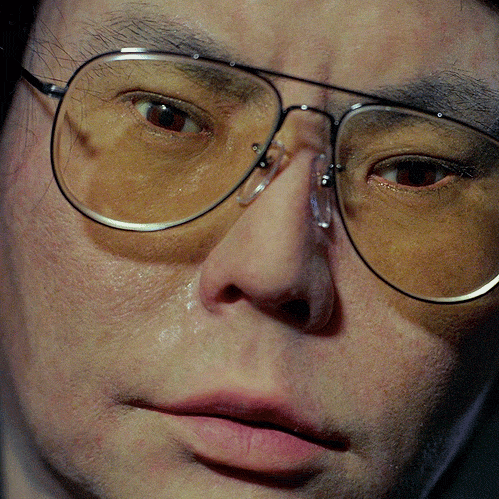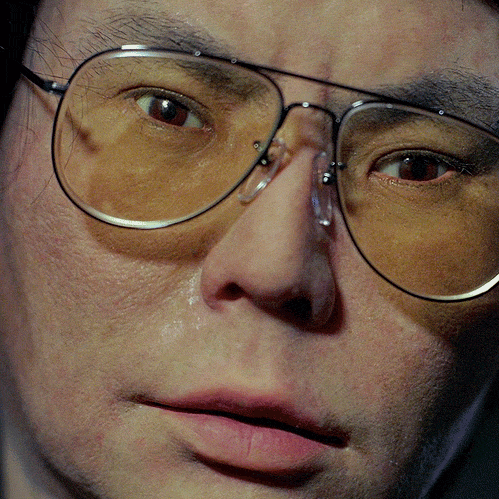
The writer’s latest effort, a profile of Y Combinator President Sam Altman, a stripling yet a strongman, reveals someone who has almost no patience for or interest in most people yet wants to save the world–or something.
It’s not a hit job, as Altman really has no intent to offend or injure, but it vivisects Silicon Valley’s Venture Capital culture and the outrageous hubris of those insulated inside its wealth and privilege, the ones who nod approvingly while watching Steve Jobs use Mahatma Gandhi’s image to sell wildly marked-up electronics made by sweatshop labor, and believe they also can think different.
When envisioning the future, Altman sees perhaps a post-scarcity, automated future where a few grand a year of Universal Basic Income can buy the jobless a bare existence (certainly not the big patch of Big Sur he owns), or maybe there’ll be complete societal collapse and the VC wunderkind can flee the carnage by jetting with that misery Peter Thiel to the safety of his New Zealand spread (though grisly death seems preferable). Either or. More or less.
Three quick excerpts from the piece follow.
The immediate challenge is that computers could put most of us out of work. Altman’s fix is YC Research’s Basic Income project, a five-year study, scheduled to begin in 2017, of an old idea that’s suddenly in vogue: giving everyone enough money to live on. Expanding on earlier trials in places such as Manitoba and Uganda, YC will give as many as a thousand people in Oakland an annual sum, probably between twelve thousand and twenty-four thousand dollars.
The problems with the idea seem as basic as the promise: Why should people who don’t need a stipend get one, too? Won’t free money encourage indolence? And the math is staggering: if you gave each American twenty-four thousand dollars, the annual tab would run to nearly eight trillion dollars—more than double the federal tax revenue. However, Altman told me, “The thing most people get wrong is that if labor costs go to zero”—because smart robots have eaten all the jobs—“the cost of a great life comes way down. If we get fusion to work and electricity is free, then transportation is substantially cheaper, and the cost of electricity flows through to water and food. People pay a lot for a great education now, but you can become expert level on most things by looking at your phone. So, if an American family of four now requires seventy thousand dollars to be happy, which is the number you most often hear, then in ten to twenty years it could be an order of magnitude cheaper, with an error factor of 2x. Excluding the cost of housing, thirty-five hundred to fourteen thousand dollars could be all a family needs to enjoy a really good life.”
On the far side of a fire pit, two founders of Shypmate, an app that links you to airline passengers who will cheaply carry your package to Ghana or Nigeria, were commiserating. Kwadwo Nyarko said, “We’re at the mercy of travellers who never have as much space in their luggage as they said.” Perry Ogwuche murmured, “YC tells us, ‘Talk to your customers,’ but it’s hard to find our customers.” Altman walked over to engage them, dutiful as a birthday-party magician. “So what are your hobbies?” he asked. Nonplussed, Ogwuche said, “We work and we go to the gym. And what are yours?”
“Well, I like racing cars,” Altman said. “I have five, including two McLarens and an old Tesla. I like flying rented planes all over California. Oh, and one odd one—I prep for survival.” Seeing their bewilderment, he explained, “My problem is that when my friends get drunk they talk about the ways the world will end. After a Dutch lab modified the H5N1 bird-flu virus, five years ago, making it super contagious, the chance of a lethal synthetic virus being released in the next twenty years became, well, nonzero. The other most popular scenarios would be A.I. that attacks us and nations fighting with nukes over scarce resources.” The Shypmates looked grave. “I try not to think about it too much,” Altman said. “But I have guns, gold, potassium iodide, antibiotics, batteries, water, gas masks from the Israeli Defense Force, and a big patch of land in Big Sur I can fly to.”
Altman’s mother, a dermatologist named Connie Gibstine, told me, “Sam does keep an awful lot tied up inside. He’ll call and say he has a headache—and he’ll have Googled it, so there’s some cyber-chondria in there, too. I have to reassure him that he doesn’t have meningitis or lymphoma, that it’s just stress.” If the pandemic does come, Altman’s backup plan is to fly with his friend Peter Thiel, the billionaire venture capitalist, to Thiel’s house in New Zealand. Thiel told me, “Sam is not particularly religious, but he is culturally very Jewish—an optimist yet a survivalist, with a sense that things can always go deeply wrong, and that there’s no single place in the world where you’re deeply at home.”
Four years ago, on a daylong hike with friends north of San Francisco, Altman relinquished the notion that human beings are singular. As the group discussed advances in artificial intelligence, Altman recognized, he told me, that “there’s absolutely no reason to believe that in about thirteen years we won’t have hardware capable of replicating my brain. Yes, certain things still feel particularly human—creativity, flashes of inspiration from nowhere, the ability to feel happy and sad at the same time—but computers will have their own desires and goal systems. When I realized that intelligence can be simulated, I let the idea of our uniqueness go, and it wasn’t as traumatic as I thought.” He stared off. “There are certain advantages to being a machine. We humans are limited by our input-output rate—we learn only two bits a second, so a ton is lost. To a machine, we must seem like slowed-down whale songs.”•