In a NYRB blog post, James Gleick tries to identify the invaders among us, the social bots that cajole and troll on Twitter. Who are they? Just as importantly: Who are we if we’re not quite sure if we’re communicating with something not human, or if we know we are and yet still choose to interact? An excerpt:
A well-traveled branch of futuristic fiction explores worlds in which artificial creatures—the robots—live among us, sometimes even indistinguishable from us. This has been going for almost a century now. Stepford wives. Androids dreaming of electric sheep. (Next, Ex Machina?)
Well, here they come. It’s understood now that, beside what we call the “real world,” we inhabit a variety of virtual worlds. Take Twitter. Or the Twitterverse. Twittersphere. You may think it’s a stretch to call this a “world,” but in many ways it has become a toy universe, populated by millions, most of whom resemble humans and may even, in their day jobs, behumans. But increasing numbers of Twitterers don’t even pretend to be human. Or worse, do pretend, when they are actually bots. “Bot” is of course short for robot. And bots are very, very tiny, skeletal, incapable robots—usually little more than a few crude lines of computer code. The scary thing is how easily we can be fooled.
Because the Twitterverse is made of text, rather than rocks and trees and bones and blood, it’s suddenly quite easy to make bots. Now there are millions, by Twitter’s own estimates—most of them short-lived and invisible nuisances. …
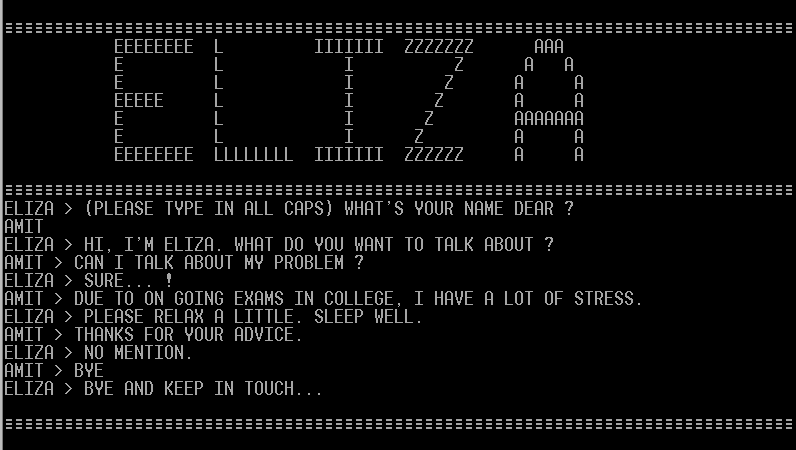
Most of these bots have all the complexity of a wind-up toy. Yet they have the potential to influence the stock market and distort political discourse. The surprising thing—disturbing, if your human ego is easily bruised—is how few bells and gears have to be added to make a chatbot sound convincing. How much computational complexity is powering our own chattering mouths? The grandmother of all chatbots is the famous Eliza, described by Joseph Weizenbaum at MIT in a 1966 paper (yes, children, Eliza is fifty years old). His clever stroke was to give his program the conversational method of a psychotherapist: passive, listening, feeding back key words and phrases, egging on her poor subjects. “Tell me more.” “Why do you feel that way?” “What makes you think [X]?” “I am sorry to hear you are depressed.” Oddly, Weizenbaum was a skeptic about “artificial intelligence,” trying to push back against more optimistic colleagues. His point was that Eliza knew nothing, understood nothing. Still the conversations could run on at impressive length. Eliza’s interlocutors felt her empathy radiating forth. It makes you wonder how often real shrinks get away with leaving their brains on autopilot.
Today Eliza has many progeny on Twitter, working away in several languages.