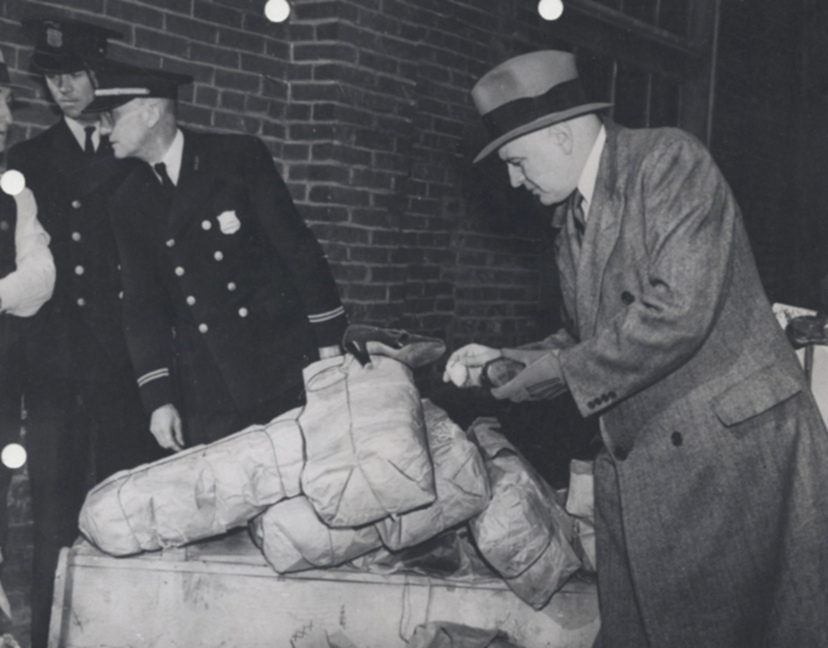
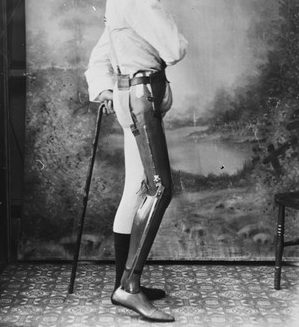
From the February 5, 1913 Brooklyn Daily Eagle:
You are currently browsing the archive for the Urban Studies category.
The term “middle class” was not always a nebulous one in America. It meant that you had arrived on solid ground and only the worst luck or behavior was likely to shake the earth beneath your feet. That’s become less and less true for four decades, as a number of factors (technology, globalization, tax codes, the decline of unions, the 2008 economic collapse, etc.) have conspired to hollow out this hallowed ground. You can’t arrive someplace that barely exists.
Middle class is now what you think you would be if you had any money. George Carlin’s great line that “the reason they call it the American Dream is because you have to be asleep to believe it” seems truer every day. It’s not so much a fear of falling anymore, but the fear of never getting up, at least not within the current financial arrangement. Those hardworking, decent people you see every day? They’re just as afraid as you are. They are you.
In the spirit of the great 1977 Atlantic article “The Gentle Art of Poverty” and William McPherson’s recent Hedgehog Review piece “Falling,” the excellent writer and film critic Neal Gabler has penned, also for the Atlantic, an essay about his “secret shame” of being far poorer than appearances would indicate. An excerpt:
I know what it is like to have to juggle creditors to make it through a week. I know what it is like to have to swallow my pride and constantly dun people to pay me so that I can pay others. I know what it is like to have liens slapped on me and to have my bank account levied by creditors. I know what it is like to be down to my last $5—literally—while I wait for a paycheck to arrive, and I know what it is like to subsist for days on a diet of eggs. I know what it is like to dread going to the mailbox, because there will always be new bills to pay but seldom a check with which to pay them. I know what it is like to have to tell my daughter that I didn’t know if I would be able to pay for her wedding; it all depended on whether something good happened. And I know what it is like to have to borrow money from my adult daughters because my wife and I ran out of heating oil.
You wouldn’t know any of that to look at me. I like to think I appear reasonably prosperous. Nor would you know it to look at my résumé. I have had a passably good career as a writer—five books, hundreds of articles published, a number of awards and fellowships, and a small (very small) but respectable reputation. You wouldn’t even know it to look at my tax return. I am nowhere near rich, but I have typically made a solid middle- or even, at times, upper-middle-class income, which is about all a writer can expect, even a writer who also teaches and lectures and writes television scripts, as I do. And you certainly wouldn’t know it to talk to me, because the last thing I would ever do—until now—is admit to financial insecurity or, as I think of it, “financial impotence,” because it has many of the characteristics of sexual impotence, not least of which is the desperate need to mask it and pretend everything is going swimmingly. In truth, it may be more embarrassing than sexual impotence.•
Tags: Neal Gabler
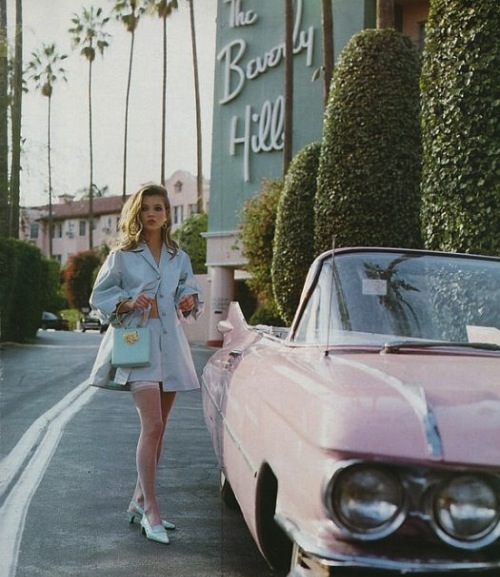
Campuses, theme parks and other small, contained areas in warm-weather locales seem like Ground Zero for driverless cars, since they’re usually well-maintained and more predictable and mappable than wide-open spaces. Modestly-sized neighborhoods may be in the same category. Case in point: Beverly Hills would like autonomous vehicles, which could be summoned with a smartphone, to supplement its current public-transportation system.
From James Vincent at The Verge:
Futurists have suggested that one day, self-driving cars might augment or even replace public transport, but for the town elders of Beverly Hills, this future is nearer than you’d think. Earlier this month, the city’s council voted unanimously to create a program to “develop autonomous vehicles as public transportation.”
The council’s vision is for self-driving vehicles to provide “on-demand, point-to-point transportation,” with citizens “requesting a ride using their smartphone.” The shuttles wouldn’t replace public transportation, but augment it, with Beverly Hills Mayor John Mirisch describing how autonomous vehicles would solve the “first/last mile” problem for residents using the city’s future subway — the Purple Line Extension — to get in and out of the city.
“This is a game-changer for Beverly Hills and, we hope, for the region,” said Mirisch in a press release. “Beverly Hills is the perfect community to take the lead to make this technology a reality. It is now both feasible and safe for autonomous cars to be on the road.”•
Tags: James Vincent
 Chemtrails are bullshit, of course, but in 1950s America, there was definitely something in the air.
Chemtrails are bullshit, of course, but in 1950s America, there was definitely something in the air.
That was especially true if you lived in desert areas in which the U.S. government was conducting A-bomb tests. Windstorms at just the wrong moment could cause havoc, blowing radioactive mist into unsuspecting nearby communities.
One such bomb, nicknamed “Harry,” was detonated in Nevada on May 19, 1953, with gusts carrying its fallout 135 miles, running headlong into 5,000 people, including those on the set of Howard Hughes’ film The Conqueror. Legend has it that a cancer cluster among cast and crew was the result, although that seems more urban legend than medical fact. Nonetheless, some citizens were outraged by the recklessness, and the bomb was rechristened “Dirty Harry” in retrospect.
A month earlier, the Atomic Energy Commission had carried out another detonation in same state. Just after the explosion, a pair of radio-controlled planes carrying mice and monkeys were flown through the radioactive cloud. The strange scene, which was conducted in the name of biomedical research, was recorded in an article in the April 6, 1953 Brooklyn Daily Eagle.
Computer matchmaking dates back long before “Language Style Matching,” all the way to the 1950s, in Canada at least, when singles experimented with IBM punch-card yenta-ing. It was, as you might guess, rudimentary, as hook-ups encouraged by the machines (based largely on height and age and hair color) still had to be arranged via rotary phone. By 1966, Gene Shalit and his mustache headed to Harvard to report for Look magazine on a computer-enabled, pre-Tinder bacchanal sweeping elite American colleges. The opening of Shalit’s Borscht Belt-New Journalism mashup for the long-defunct title:
Out of computers, faster than the eye can blink, fly letters stacked with names of college guys and girls–taped, scanned, checked and matched. Into the mails speed the compatible pairs, into P.O. boxes at schools across the land. Eager boys grab their phones… anxious coeds wait in dorms … a thousand burrrrrrrings jar the air . . . snow-job conversations start, and yeses are exchanged: A nationwild dating spree is on. Thousands of boys and girls who’ve never met plan weekends together, for now that punch-card dating’s here, can flings be far behind? And oh, it’s so right, baby. The Great God Computer has sent the word. Fate. Destiny. Go-go-go. Call it dating, call it mating, it flashed out of the minds of Jeff Tarr and Vaughn Morrill, Harvard undergraduates who plotted Operation Match, the dig-it dating system that ties up college couples with magnetic tape. The match mystique is here: In just nine months, some 100,000 collegians paid more than $300,000 to Match (and to its MIT foe, Contact) for the names of at least five compatible dates. Does it work? Nikos Tsinikas, a Yale senior, spent a New Haven weekend with his computer-Matched date, Nancy Schreiber, an English major at Smith. Result, as long date’s journey brightened into night: a bull’s-eye for cupid’s computer.•
Holy fuck, someone should have punched Gene Shalit right in the handlebar. Interesting though, despite the woeful writing, is that proto-Zuckerbergs were climbing the Ivy 50 years ago, trying to transform strange faces into friends. In a decade, “smart” romance had been monetized and become somewhat more sophisticated, but Moore’s Law clearly had a ways to go before it could truly be brought to bear on mating.
While today’s dating apps are much more algorithmically adept, it still feels like we’re in the early stages of machine-assisted love. Will the continuous development of language analysis and AI “eyes” be able to identify our cues even before we do? What does love at first sight mean in an age of visual-recognition systems?
In “When Dating Algorithms Can Watch You Blush,” Julia M. Klein’s smart Nautilus piece, the reporter looks at the next-level work of Northwestern psychologist Eli Finkel, who acknowledges it’s unlikely there is “ever going to be an algorithm that will find your soul mate.” He’s just hoping for significant if incremental improvement. The opening:
Let’s get the basics over with,” W said to M when they met on a 4-minute speed date. “What are you studying?”
“Uh, I’m studying econ and poli sci. How about you?”
“I’m journalism and English literature.”
“OK, cool.”
“Yeah.”
They talked about where they were from (she hailed from Iowa, he from New Jersey), life in a small town, and the transition to college. An eavesdropper would have been hard-pressed to detect a romantic spark in this banal back-and-forth. Yet when researchers, who had recorded the exchange, ran it through a language-analysis program, it revealed what W and M confirmed to be true: They were hitting it off.
The researchers weren’t interested in what the daters discussed, or even whether they seemed to share personality traits, backgrounds, or interests. Instead, they were searching for subtle similarities in how they structured their sentences—specifically, how often they used function words such as it, that, but, about, never, and lots. This synchronicity, known as “language style matching,” or LSM, happens unconsciously. But the researchers found it to be a good predictor of mutual affection: An analysis of conversations involving 80 speed daters showed that couples with high LSM scores were three times as likely as those with low scores to want to see each other again.
It’s not just speech patterns that can encode chemistry. Other studies suggest that when two people unknowingly coordinate nonverbal cues, such as hand gestures, eye gaze, and posture, they’re more apt to like and understand each other. These findings raise a tantalizing question: Could a computer know whom we’re falling for before we do?•
Tags: Eli Finkel, Julia M. Klein
Robots have been able to make hamburgers for more than 50 years, but it was never before financially sensible for franchises to transition. When such work was greasy kid stuff, the positions paid little and had a high churn rate. They were beginner jobs.
Globalization, technological progress and other factors, however, have hollowed out the middle in America, so calls for minimum-wage increases in such service positions, now often treated as careers, were a natural. Equally expected is the response by fast-food company CEOs who want to keep the bottom line lean: We’ll automate.
Perhaps there’s something worse than the fear that we’ll be reduced to McJobs: What if even such low-paying positions are automated?
From Joe Kaiser at Illinois Policy:
The Fight for $15 campaign plans to target McDonald’s on April 14 as part of a new pre-Tax Day tradition, led by the Service Employees International Union, or SEIU.
Chicago is one of 300 cities worldwide where strikes and protests are scheduled. SEIU has spent $70 million on its Fight for $15 campaign. The union’s Local 73 represents more than 28,000 government workers in Illinois and Indiana.
Protestors may want to stop by the McDonald’s at Adams and Wells to meet their replacement – an automated McCafé kiosk.
The store, which is anticipating Chicago’s minimum-wage increase to $13 an hour by 2019, is testing out coffee kiosks in the restaurant instead of having employees serve it. The kiosk features a touch-pad for ordering and paying. The screen also prompts customers to answer questions about their kiosk experience, giving the impression this is something that could be adopted as an alternative to hiring. This kind of automation, which replaces a human employee with technology, is one of the unintended consequences of Chicago’s minimum-wage increase.
It may not just be a coffee machine either. Other McDonald’s locations have used self-service kiosks with touch-screens for paying. And while self-serve kiosks don’t seem too unusual, San Francisco-based Momentum Machines has created a robotic hamburger-making machine the company claims can produce 400 high-quality burgers in an hour with minimal human supervision.
A robot making a hamburger sounds a bit absurd, but the desire to circumvent artificially set wages certainly isn’t.•
Tags: Joe Kaiser

Homer Collyer, 1939.

Langley Collyer, 1946.
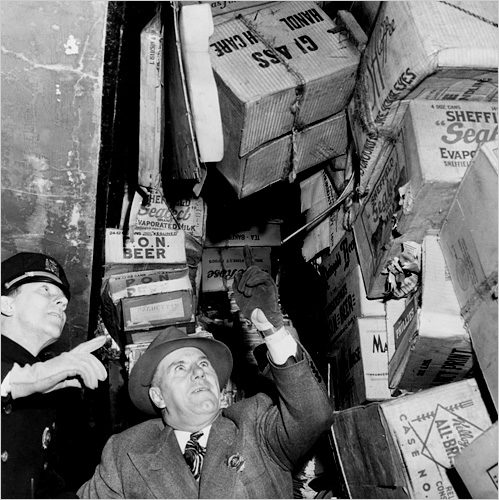
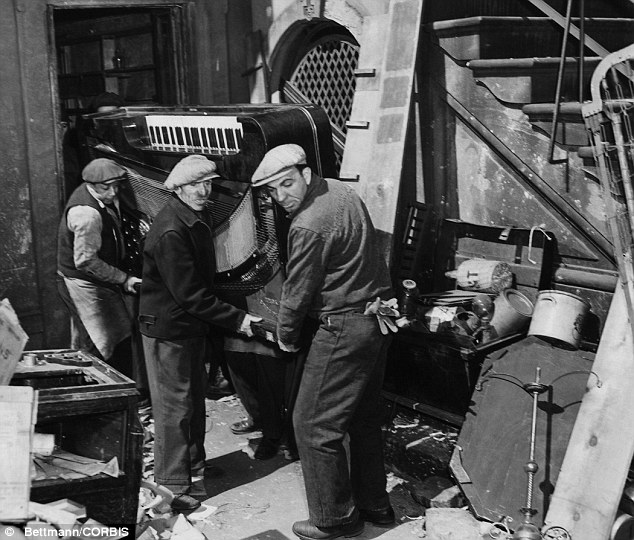

 One person can lose his mind, but nothing is madder than a couple.
One person can lose his mind, but nothing is madder than a couple.
Two souls can encourage each other to health and prosperity, but they can also nurture mutual insanity, creating a madhouse behind close doors, replacing bedroom mirrors with the funhouse kind. No living quarters in New York City history were likely crazier than the Fifth Avenue hoarder heaven that the reclusive brothers Homer and Langley Collyer called home sweet home. It contained, among many–many–other things, 240,000 pounds of garbage, 18,000 books, 17 grand pianos, eight live cats, three dressmaking dummies and two very damaged brothers.
A March 22, 1947 Brooklyn Daily Eagle article about the demise of the Collyers was published after the police had found Homer’s lifeless body seated in a chair but 18 days before they realized that Langley was just ten feet away, dead and buried under some of his favorite things.
Earlier today, I posted a piece about Russian entrepreneur Yuri Milner, who’s bankrolling an attempt at an unpeopled reconnaissance mission to Alpha Centauri. A techno-optimist the way most high flyers in Silicon Valley are, Milner believes our increasing connectedness, including the Internet of Things, will bring about a more prosperous world–even a “global brain,” which will unite us all and serve as a “global central nervous system.” That new wealth may be distributed very unevenly, but the wholesale connectivity will likely arrive sooner than later. It will be both boon and bane.
From a Reuters report Chrystia Freeland filed in 2001, just twelve days after the 9/11 attacks:
Milner almost perfectly represents a global technology elite whose frame of reference is planet Earth. He mostly lives in Moscow, but has recently purchased a palatial home in Silicon Valley. He addressed the Ukrainian conference by video link from Singapore.
From that vantage point, the most pressing issue in the world today isn’t recession and political paralysis in the West, or even the rapid development and political transformation in emerging markets, it is the technology revolution, which, in Mr. Milner’s view, is only getting started. Here are the changes he thinks are most significant:
• The Internet revolution is the fastest economic change humans have experienced, and it is accelerating. Mr. Milner said two billion people are online today. Over the next decade, he predicts that that number will more than double.
• The Internet is not just about connecting people, it is also about connecting machines, a phenomenon Mr. Milner dubbed “the Internet of things.” Mr. Milner said that five billion devices are connected today. By 2020, he thinks more than 20 billion will be.
• More information is being created than ever before. Mr. Milner asserted that as much information was created every 48 hours in 2010 as was created between the dawn of time and 2003. By 2020, that same volume of information will be generated every 60 minutes.
• People are sharing information ever more frequently. The pieces of content shared on Facebook have increased from 140 million in 2009 to 4 billion in 2011. We are even sending more e-mails: 50 billion were sent in 2006, versus 300 billion in 2010.
• The result, according to Mr. Milner, is the dominance of Internet platforms relative to traditional media. “The largest newspaper in the United States is only reaching 1 percent of the population.” he said. “That compares to Internet media, which is used by 25 percent of the population daily and growing.”
• Internet businesses are much more efficient than brick-and-mortar companies. This was one of Mr. Milner’s most striking observations, and a clue to the paradox of how we find ourselves simultaneously living in a time of what Mr. Milner views as unprecedented technological innovation but also high unemployment in the developed West. As Mr. Milner said, “Big Internet companies on average are capable of generating revenue of $1 million per employee, and that compares to 10 to 20 percent of that which is normally generated by traditional offline businesses of comparable size.” As an illustration, Mr. Milner cited Facebook, where, he said, each single engineer supports one million users.
• Artificial intelligence is part of our daily lives, and its power is growing. Mr. Milner cited everyday examples like Amazon.com’s recommendation of books based on ones we have already read and Google’s constantly improving search algorithm.
• Finally — and Mr. Milner admitted this was “a bit of a futuristic picture” — he predicted “the emergence of the global brain, which consists of all the humans connected to each other and to the machine and interacting in a very unique and profound way, creating an intelligence that does not belong to any single human being or computer.”•
Tags: Chrystia Freeland, Yuri Milner
If I was Gay Talese, I would have called the police.
The legendary journalist was contacted several decades ago by motel-owning Colorado voyeur Gerald Foos, who spied on his guests’ sexual behavior through vents of his own design carefully hidden atop the rooms. The peeping Tom rationalized his aberrant behavior by assuming the mantle of science, believing himself more Kinsey than kinky. It was self-deception–the cataloging of couplings, the sociological musings he attached to the private acts he’d witnessed, the whole thing. What’s worse is his actions unintentionally triggered a murder, which he watched from above, like a god not given to interfering in the lives of mere mortals. His story is an extreme psychological portrait, but one that doesn’t seem especially relatable even in this age of ubiquitous cameras. Most perverts still draw the line at consent. The ones who don’t, like those who downloaded naked photos of Erin Andrews or hacked selfies from the “Fappening,” can’t talk away their intrusions as Foos does (e.g., the spied upon will never learn they were victimized).
Talese was along for the ride, not only reading the lusty ledgers and allowing the invasions of privacy to continue apace, but also having a peep or two himself during a visit to Aurora. When he finds out about the killing, he still doesn’t turn in Foos, living up to their initial contract that commanded the writer would never speak of his subject’s conduct. Clearly, though, it wasn’t paper but curiosity and fear that guided the reporter’s suspect behavior. “Where was I in all this?” Talese asks near end of his New Yorker article about the experience, but I don’t think he gets to answer that question.
An excerpt:
What he saw was a murder. It occurred in Room 10.
He described the occupants as a young couple who had rented a room for several weeks. The man, in his late twenties, was about a hundred and eighty pounds. The Voyeur deduced from his eavesdropping that he was a college dropout and a small-time drug dealer. The girl was blond, with a 34D bust. (Foos had gone into the room while the couple was out and checked her bra size, something he says he did often.) Foos devoted pages and pages to an approving account of the couple’s vigorous sex life. The journal also described people coming to the door of Room 10 to buy drugs. This upset Foos, but he did not notify the police. In the past, he had reported drug dealing in his motel when he saw it, but the police took no action, because he could not identify himself as an eyewitness to his complaints.
One afternoon, Foos saw the man in Room 10 sell drugs to a few young boys. This incensed him. He wrote in the journal, “After the male subject left the room that afternoon, the voyeur entered his room. . . . The voyeur, without any guilt, silently flushed all the remaining drugs and marijuana down the toilet.” He had flushed motel guests’ drugs several times before, with no repercussions.
This time, the man in Room 10 accused his girlfriend of stealing the drugs. The journal continues:
After fighting and arguing for about one hour, the scene below the voyeur turned to violence. The male subject grabbed the female subject by the neck and strangled her until she fell unconscious to the floor. The male subject, then in a panic, picked up all his things and fled the vicinity of the motel.
The voyeur . . . without doubt . . . could see the chest of the female subject moving, which indicated to the voyeur that she was still alive and therefore O.K. So, the voyeur was convinced in his own mind that the female subject had survived the strangulation assault and would be all right, and he swiftly departed the observation platform for the evening.
Foos reasoned that he couldn’t do anything anyway, “because at this moment in time he was only an observer and not a reporter, and really didn’t exist as far as the male and female subjects were concerned.”
The next morning, a maid ran into the motel office and said that a woman was dead in Room 10. Foos wrote that he immediately called the police. When officers arrived, he gave them the drug dealer’s name, his description, and his license-plate number. He did not say that he had witnessed the murder.
Foos wrote, “The voyeur had finally come to grips with his own morality and would have to forever suffer in silence, but he would never condemn his conduct or behavior in this situation.”
The next day, the police returned and told Foos that the drug dealer had been using a fake name and had been driving a stolen car.
I came upon this account in Foos’s typescript a few years after I’d visited him in Aurora—and nearly six years after the murder. I was shocked, and surprised that Foos had not mentioned the incident to me earlier. It almost seemed as if he regarded it as just another day in the attic. But, as I thought about it, his response—the observation that he “really didn’t exist as far as the male and female subjects were concerned”—was consistent with his sense of himself as a fractured individual. He was also desperately protective of his secret life in the attic. If the police had grilled him and decided that he knew more than he was telling, they might have obtained a search warrant, and the consequences could have been catastrophic.
I called Foos right away to ask about the situation. I wanted to find out whether he realized that, in addition to witnessing a murder, he might have, in some way, caused it.
He was reluctant to say more than he had written in his journal, and he reminded me that I had signed a confidentiality agreement. I spent a few sleepless nights, asking myself whether I ought to turn Foos in. But I reasoned that it was too late to save the drug dealer’s girlfriend. Also, since I had kept the Voyeur’s secret, I felt worrisomely like a co-conspirator.•
Tags: Gay Talese, Gerald Foos
Alec Ross, author of The Industries of the Future, was asked in a Knowledge@Wharton interview about the next wave of work and wealth, and he echoed the sentiment in Tyler Cowen’s Average Is Over, noting that only those committed to continued education and possessing a flexible spirit will get ahead. Well, that’s good to know, but one obvious thing that often goes unmentioned in these discussions is what happens to the very large number of people who won’t be able to adapt to rapid change and do get left behind. That’s likely and must somehow be addressed.
An excerpt:
Question:
As robots and codification and all of these other industries that you identify in the book become more prominent, how do you feel that’s going to change the world balance of power? How does that change the global economy and who has power and who doesn’t?
Alec Ross:
That’s a tremendous question. First of all, I’d put it into a certain kind of binary. The first is within the architecture of the 196 sovereign nation states, and the second is within those nation states, what kinds of individuals do well and what kinds of individuals do poorly.
You can live in a country that is prospering, but you can be doing very well or you could be doing very poorly. Or you could be living in a country that’s floundering, and you might be able to be doing pretty well. The principle political and economic binary of the 20th century was right versus left. In the 21st century, I think it’s open versus closed, defining open as upward economic mobility not confined to elites; social and cultural and religious norms not set from a central authority and broadly rights respecting for women, minorities of all type and what have you.
I believe that the centers of innovation and the wealth creation and job creation that come from that will be in the more open societies for the industries of the future. People conglomerating around what will probably be ten to 15 major centers over the next fifteen years. We already see this in development now. The more open societies will be those that compete and succeed most effectively.
Looking at this on an individual level, it’s going to be a terrible time to be mediocre at your job if you’re in a high-cost labor market. It’s an absolutely brutal truth. When people in Baltimore are competing against people in Bangalore, not just based on cost of labor but also quality of labor, which is now increasingly going to be the case, being more middle class or working class in the United States or Western Europe isn’t going to mean you’re starting life on second base to the degree that it did in the past.
You’ve got to be a committed lifelong learner. You’ve got to be adaptable. Otherwise you’re going to be left behind even if your country is producing substantial growth.•
Tags: Alec Ross
Two excerpts follow from 1960s Psychedelic Review articles about the drug culture of that era, penned by Timothy Leary and Stewart Brand.
Before there was turnt, there was turned-on, the term for LSD experimentation taken from the Timothy Leary-Marshall McLuhan co-created mantra “Turn on, Tune in, Drop Out.” Thanks to some fakakta reasoning, Leary was allowed, during his Harvard professor days, to do acid tests on Massachusetts prison inmates, the belief being that the trip would help them arrive at rehabilitation. The subjects were wary of the good doctor, and for good reason, though by Leary’s telling everything went well overall. The guru recalled the experience in an article in the 1969 Psychedelic Review. An excerpt:
I’ll never forget that morning. After about half an hour, I could feel the effect coming up, the loosening of symbolic reality, the feeling of humming pressure and space voyage inside my head, the sharp, brilliant, brutal, intensification of all the senses. Every cell and every sense organ was humming with charged electricity. I felt terrible. What a place to be on a gray morning! In a dingy room, in a grim penitentiary, out of my mind. I looked over at the man next to me, a Polish embezzler from Worcester, Massachusetts. I could see him so clearly. I could see every pore in his face, every blemish, the hairs in his nose, the incredible green-yellow enamel of the decay in his teeth, the wet glistening of his frightened eyes. I could see every hair in his head, as though each was as big as an oak tree. What a confrontation! What am I doing here, out of my mind, with this strange mosaic-celled animal, prisoner, criminal?
I said to him, with a weak grin, How are you doing, John? He said, I feel fine. Then he paused for a minute, and asked, How are you doing, Doc? I was about to say in a reassuring psychological tone that I felt fine, but I couldn’t, so I said, I feel lousy. John drew back his purple pink lips, showed his green-yellow teeth in a sickly grin and said, What’s the matter, Doc? Why you feel lousy? I looked with my two microscopic retina lenses into his eyes. I could see every line, yellow spider webs, red network of veins gleaming out at me. I said, John, I’m afraid of you. His eyes got bigger, then he began to laugh. I could look inside his mouth, swollen red tissues, gums, tongue, throat. Well that’s funny Doc, ’cause I’m afraid of you. We were both smiling at this point, leaning forward. Doc, he said, why are you afraid of me? I said, I’m afraid of you, John, because you’re a criminal. I said, John, why are you afraid of me? He said, I’m afraid of you Doc because you’re a mad scientist. Then our retinas locked and I slid down into the tunnel of his eyes, and I could feel him walking around in my skull and we both began to laugh. And there it was, that dark moment of fear and distrust, which could have changed in a second to become hatred, terror. We’d made the love connection. The flicker in the dark. Suddenly, the sun came out in the room and I felt great and I knew he did too.
We had passed that moment of crisis, but as the minutes slowly ticked on, the grimness of our situation kept coming back in microscopic clarity. There were the four of us turned-on, every sense vibrating, pulsating with messages, two billion years of cellular wisdom, but what could we do trapped within the four walls of a gray hospital room, barred inside a maximum security prison? Then one of the great lessons in my psychedelic training took place. One of the four of us was a Negro from Texas, jazz saxophone player, heroin addict. He looked around with two huge balls of ocular white, shook his head, staggered over to the record player, put on a record. It was a Sonny Rollins record which he’d especially asked us to bring. Then he lay down on the cot and closed his eyes. The rest of us sat by the table while metal air from the yellow saxophone, spinning across copper electric wires, bounced off the wails of the room. There was a long silence. Then we heard Willy moaning softly, and moving restlessly on the couch. I turned and looked at him, and said, Willy, are you all right? There was apprehension in my voice. Everyone in the room swung their heads anxiously to look and listen for the answer. Willy lifted his head, gave a big grin, and said, Man, am I all right? I’m in heaven and I can’t believe it! Here I am in heaven man, and I’m stoned out of my mind, and I’m swinging like I’ve never before and it’s all happening in prison, and you ask me man, am I all right. What a laugh! And then he laughed, and we all laughed, and suddenly we were all high and happy and chuckling at what we had done, bringing music, and love, and beauty, and serenity, and fun, and the seed of life into that grim and dreary prison. …
As I rode along the highway, the tension and the drama of the day suddenly snapped off and I could look back and see what we had done. Nothing, you see, is secret in prison, and the eight of us who had assembled to take drugs together in a prison were under the gaze of every convict in the prison and every guard, and within hours the word would have fanned through the invisible network to every other prison in the state. Grim Walpole penitentiary. Grey, sullen-walled Norfolk.
Did you hear? Some Harvard professors gave a new drug to some guys at Concord. They had a ball. It was great. It’s a grand thing. It’s something new. Hope. Maybe. Hope. Perhaps. Something new. We sure need something new. Hope.•
Peyote has historically been central to the Native American church meeting. In a 1967 Psychedelic Review article, Stewart Brand, Prankster and prophet, wrote of one such congregation he attended. An excerpt:
The meeting is mandala-form, a circle with a doorway to the east. The roadman will sit opposite the door, the moon-crescent altar in front of him. To his left sits the cedarman, to his right the drummer. On the right side as you enter will be the fireman. The people sit around the circle. In the middle is the fire.
A while after dark they go in. This may be formal, filling in clockwise around the circle in order. The roadman may pray outside beforehand, asking that the place and the people and the occasion be blessed.
Beginning a meeting is as conscious and routine as a space launch countdown. At this time the fireman is busy starting the fire and seeing that things and people are in their places. The cedarman drops a little powder of cedar needles and little balls, goes down the quickest. In all cases, the white fluff should be removed. There is usually a pot of peyote tea, kept near the fire, which is passed occasionally during the night. Each person takes as much medicine as he wants and can ask for more at any time. Four buttons is a common start. Women usually take less than the men. Children have only a little, unless they are sick.
Everything is happening briskly at this point. People swallow and pass the peyote with minimum fuss. The drummer and roadman go right into the starting song. The roadman, kneeling on one or both knees, begins it with the rattle in his right hand. The drummer picks up the quick beat, and the roadman gently begins the song. His left hand holds the staff, a feather fan, and some sage. He sings four times, ending each section with a steady quick rattle as a signal for the drummer to pause or re-wet the drumhead before resuming the beat. Using his thumb on the drumhead, the drummer adjusts the beat of his song. When the roadman finishes he passes the staff, gourd, fan and sage to the cedarman, who sings four times with the random drumming. So it goes, the drum following the staff to the left around the circle, so each man sings and drums many times during the night.•
I’ve always traced the War on Drugs in the U.S. to the Nixon Administration, but British journalist Johann Hari, author of the book Chasing the Scream, dates it to the end of Prohibition, particularly to bureaucrat Harry Anslinger, a stern-faced Fed who looked like Mussolini as played by George C. Scott, who later mentored Sheriff Joe Arpaio of Tent City infamy. Hari also reveals how intertwined crackdown was (and is) with racism. No shocker there.
The so-called War has been a huge failure tactically and financially and has criminalized citizens for no good reason. All the while, there’s been a tacit understanding that millions of Americans are hooked on Oxy and the like, dousing their pain with a perfectly legal script. These folks are far worse off than pot smokers, but it’s the latter who are still afoul of the law in most states. I’m personally completely opposed to recreational drug use, but I feel even more contempt for the War on Drugs. It’s done far more harm than good. Decriminalize drugs that can be used in moderation, send users of harder drugs to rehab and only imprison those selling drugs to minors. It’s not ideal, but I think it’s a far saner solution. Or try something else; just make it less destructive.
From a LARB Q&A David Breithaupt conducted with Hari, an excerpt about the groups that inspired Anslinger’s folly, a seemingly never-ending waterloo:
He built the war on drugs around the three groups he hated most. The first was African-Americans. This is a man who was so racist that he was regarded as crazily so during the 1920s. His own Senator said he should have to resign because he used the “N word” so much in official memos. He believed that drugs were deranging African-Americans and leading them to attack whites and impregnate white women.
The second group was drug addicts. Anslinger believed that addicts were “contagious” and had to be “quarantined” — cut off from the rest of humanity. These first two groups came together, in his mind, in the form of the great jazz singer, Billie Holiday, who was his worst nightmare: a drug-addicted African-American woman challenging white supremacy. He was obsessed with her. In the book, I tell the story of how he stalked her, playing a key role in her death. The story of how Billie — and so many other Americans at the time — resisted Anslinger and the early drug war is one of the most inspiring I know.
The third group Anslinger hated was the Mafia. And here’s a complexity to the story: he was one of the first senior figures in federal government to realize the Mafia was real. It’s hard to believe now, but the Mafia was seen as an urban myth — like Bigfoot or the Loch Ness Monster. But Anslinger had met these wiseguys as a young man. He knew they were real, and he wanted to destroy them. The tragedy is that the policy he believed would destroy them — drug prohibition — was, in fact, the biggest gift they received in the 20th century. He transferred the enormous industry in drugs from the people who used to control it — doctors and pharmacists — into the hands of organized crime. That’s what prohibition does. Milton Friedman, the Nobel Prize-winning economist, said: “Al Capone was the product of alcohol prohibition. The Crips and the Bloods [and, he might well have added, Pablo Escobar and El Chapo] are the product of drug prohibition.”•
Tags: David Breithaupt
I’ve mentioned before that the final 5% of perfecting driverless cars will be likely be more difficult than the first 95%. Those final digits make all the difference, of course, since, while aspects of automation can be useful, the technology is only transformational if it allows drivers to become passengers. When we can take our hands off the wheel and eyes off the road, the effects on the highway and the economy will be seismic. Consumers will probably have cheap rides a smartphone message away, and truckers, hacks and delivery people may be out of a job.
In a New Statesman article, Christian Wolmar argues that autonomous is a myth and that we will never own driverless cars. Well, someone will someday since nothing about the technology is theoretically impossible, even if the final strides of the marathon are arduous. His argument that driverless cars are as likely as jetpacks seems an exaggeration and his proof not entirely convincing. An excerpt:
The driverless car does not stand up to scrutiny. When pressed, Musk conceded that the “fully autonomous” car that he said would be ready by 2018 would not be completely automatic, nor would it go on general sale. There is a pattern. Whenever I ask people in the field what we can expect by a certain date, it never amounts to anything like a fully autonomous vehicle but rather a set of aids for drivers.
This is a crucial distinction. For this technology to be transformational, the cars have to be 100 per cent autonomous. It is worse than useless if the “driver” has to watch over the controls, ready to take over if an incident seems likely to occur. Such a future would be more dangerous than the present, as our driving skills will have diminished, leaving us less able to react. Google notes that it can take up to 17 seconds for a person to respond to alerts of a situation requiring him or her to assume control of the vehicle.
What is this technology for? The widespread assumption that driverless cars will be a shared resource, like the London Santander Cycles, is groundless. People like owning their personal vehicle because it is always available and can be customised to ensure that the child seat is properly in place and the radio tuned to Magic. Google may be right that a few parking lots will become redundant but it has no answer for the possibility that autonomy will encourage more vehicles on to the road.
The danger of all the hype is that politicians will assume that the driverless revolution obviates the need to search for solutions to more urgent problems, such as congestion and pollution. Why bother
to build infrastructure, such as new Tube lines or tram systems, or to push for road pricing, if we’ll all end up in autonomous pods? Google all but confesses that its autonomous cars are intended to be an alternative to public transport – the opposite of a rational solution to the problems that we face.•
Tags: Christian Wolmar
Capitalism will be just fine, though we’re fucked, very fucked.
In all seriousness, I think economic systems will look very different in the year 2100, when the vast majority of us are gone. 3D printing may have a huge impact on manufacturing, decentralizing it the way media has been. Scarcity-reducing automation will also be a great boon and bane simultaneously, taking much drudgery from our hands–but also paychecks. AI and robotics may not be destabilizing only for workers but for capital as well. Why, exactly, would anyone need to own a fleet of driverless cars or a lights-out factory? Couldn’t such outfits be self-owned and self-sustained?
But while markets will probably be very different, I think they’re stubborn things. I don’t believe they began as an accident but because of something deeply embedded in us–something evolutionary. They may be transformed, but I would guess they’ll persist.
Economic sociologist Wolfgang Streeck is far more dubious about the future of capitalism, believing we’re watching the system run aground. The title of his recent essay in the Socio-Economic Review doesn’t mince words: “On the Dismal Future of Capitalism.” The opening:
The writing is on the wall, and has been for some time; we must only learn to read it. The message is: capitalism is a historical social formation; it has not just a beginning but also an end.1 Three trends have run in parallel since the 1970s, throughout the family of rich capitalist democracies: declining growth, rising inequality of income and wealth and rising debt—public, private and total. Today the three seem to have become mutually reinforcing: low growth contributes to inequality by intensifying distributional conflict; inequality dampens growth by curbing effective demand; high levels of existing debt clog credit markets and increase the risk of financial crises; an overgrown financial sector both results from and adds to economic inequality etc. Already the last growth cycle before 2008 was more fake than real2 and post-2008 recovery remains anaemic at best, also because Keynesian stimulus, monetary or fiscal, fails to work in the face of unprecedented amounts of accumulated debt. Note that we are talking about long-term trends, not just a momentary unfortunate coincidence, and indeed about global trends, affecting the capitalist system as a whole and as such. Nothing is in sight that seems only nearly powerful enough to break the three trends, deeply ingrained and densely intertwined as they have become.
Moreover, looking back we see a sequence of political-economic crises that began with in- flation in the 1970s, followed by an explosion of public debt in the 1980s and by rapidly rising private debt in the subsequent decade, resulting in the collapse of financial markets in 2008. This sequence, again, was by and large the same for all major capitalist countries, whose economies have never really been in equilibrium since the end of postwar growth. All three crises began and ended in the same way: inflation, public debt and private debt initially served as expedient political solutions to distributional conflicts between capital and labour (and sometimes third parties such as raw material producers), until they became problems themselves: inflation in the early 1980s, public debt in a first consolidation phase in the 1990s, and private debt after 2008. Today’s political fix is called ‘quantitative easing’: essentially the printing of money by treasuries and central banks to keep interest rates down and accumulated debt sustainable, as well as prevent a stagnant economy from sliding into deflation, at the price of more inequality and of new bubbles in asset markets building and, eventually, collapsing.
The fundamental nature of the crisis is reflected in the extent to which the captains of capitalism have lost orientation and find themselves reduced to devising ever new provisional stopgaps until the next unpleasant surprise catches up with them. The wizards have become clueless. How long can quantitative easing go on? Is deflation the problem or inflation? How does one know a bubble before it blows up? Is growth restored through spending or through cutting back on spending? Is stricter financial regulation conducive or harmful to growth? Until the mid-1970s, growth was to result from redistribution from the top to the bottom; then, when Keynesianism was succeeded by Hayekianism, the opposite was true and markets were to be set free to redistribute from the bottom to the top. Now, seven years after the disaster of 2008, there is still no new growth formula and confusion rules the day. State-administered capitalism has failed—that is, was rejected by the owners of capital as too costly for them, to be replaced with free-market capitalism, which has also failed. For the time being, central banks act as regents waiting for a new ruler. But who would this be, and what would be his recipe for holding the capitalist enterprise together?
I suggest that after more than 200 years, capitalism has become unsustainable as a result of having become ungovernable.•
Tags: Wolfgang Streeck
America is no doubt plagued by ridiculous wealth inequality, but China, an authoritarian capitalist state, is no slouch in this area. There are copious reason for multimillionaires and billionaires minted in that nation to want to move their loved ones abroad, and one is that many of the industries that have enabled their filthy lucre have also blighted their homeland. These captains of industry have used their windfalls to disappear their children from the world’s highest cancer rates and unbreathable air, stashing them in America or Canada, where their conspicuous spending has heretofore received fewer sideways glances than it would have in the motherland.
The Chinese elite and their super-rich kids (the “Golden Generation“) have left a mark on the cost of living in Vancouver in much the same way that money from abroad has made New York City all but unlivable for much of the 99%. Dan Levin of the NYT has a smart article about the lush life of “fuerdai” inside British Columbia’s largest city. An excerpt:
Many of Vancouver’s young supercar owners are known as fuerdai, a Mandarin expression, akin to trust-fund kids, that means “rich second generation.” In China, where the superrich are widely criticized as being corrupt and materialistic, the term provokes a mix of scorn and envy.
The fuerdai have brought their passion for extravagance to Vancouver. White Lamborghinis are popular among young Chinese women; the men often turn in their leased supercars after a few months for a newer, cooler status symbol.
Hundreds of young Chinese immigrants, along with a handful of Canadian-born Chinese, have started supercar clubs whose members come together to drive, modify and photograph their flashy vehicles, providing alluring eye candy for their followers on social media.
The Vancouver Dynamic Auto Club has 440 members, 90 percent of whom are from China, said the group’s 27-year-old founder, David Dai. To join, a member must have a car that costs over 100,000 Canadian dollars, or about $77,000. “They don’t work,” Mr. Dai said of Vancouver’s fuerdai. “They just spend their parents’ money.”
Occasionally, the need for speed hits a roadblock. In 2011, the police impounded a squadron of 13 Lamborghinis, Maseratis and other luxury cars, worth $2 million, for racing on a metropolitan Vancouver highway at 125 miles per hour. The drivers were members of a Chinese supercar club, and none were older than 21, according to news reports at the time.
On a recent evening, an overwhelmingly Chinese crowd of young adults had gathered at an invitation-only Rolls-Royce event to see a new black-and-red Dawn convertible, base price $402,000. It is the only such car in North America.
Among the curious was Jin Qiao, 20, a baby-faced art student who moved to Vancouver from Beijing six years ago with his mother. During the week, Mr. Jin drives one of two Mercedes-Benz S.U.V.s, which he said were better suited for the rigors of daily life.
But his most prized possession is a $600,000 Lamborghini Aventador Roadster Galaxy, its exterior custom wrapped to resemble outer space.•
Tags: Dan Levin
While I don’t think the Singularity is upon us, mass automation could very well be. For all the good Weak AI can do for production, it will likely force us to reconsider politics, economics and even the meaning of being human.
It’s best, though, to be circumspect when considering the impact thus far of robotics. While it’s probably safe to assume machines have contributed to the middle-class decline in the U.S., there are other considerable factors, including tax codes. As far as the recent Case-Deaton findings about a spike in the death rate among white, middle-aged Americans, the wide availability of opioids has probably been as much the culprit as the decline of manufacturing. Tax codes and drug restrictions can be shifted, however, whereas automation is pointed in only one direction–and that’s up. If jobs of similar quantity and quality aren’t created to replace the vanished ones, something will have to give.
From Moshe Y. Vardi in the Guardian:
The US economy has been performing quite poorly for the bottom 90% of Americans for the past 40 years. Technology is driving productivity improvements, which grow the economy. But the rising tide is not lifting all boats, and most people are not seeing any benefit from this growth. While the US economy is still creating jobs, it is not creating enough of them. The labor force participation rate, which measures the active portion of the labor force, has been dropping since the late 1990s.
While manufacturing output is at an all-time high, manufacturing employment is today lower than it was in the later 1940s. Wages for private nonsupervisory employees have stagnated since the late 1960s, and the wages-to-GDP ratio has been declining since 1970. Long-term unemployment is trending upwards, and inequality has become a global discussion topic, following the publication of Thomas Piketty’s 2014 book Capital in the Twenty-First Century.
Most shockingly, economists Angus Deaton, winner of the 2015 Nobel memorial prize in economic science, and Anne Case found that mortality for white middle-aged Americans has been increasing over the past 25 years, due to an epidemic of suicides and afflictions stemming from substance abuse.
Is automation, driven by progress in technology, in general, and artificial intelligence and robotics, in particular, the main cause for the economic decline of working Americans?•
Tags: Moshe Y. Vardi
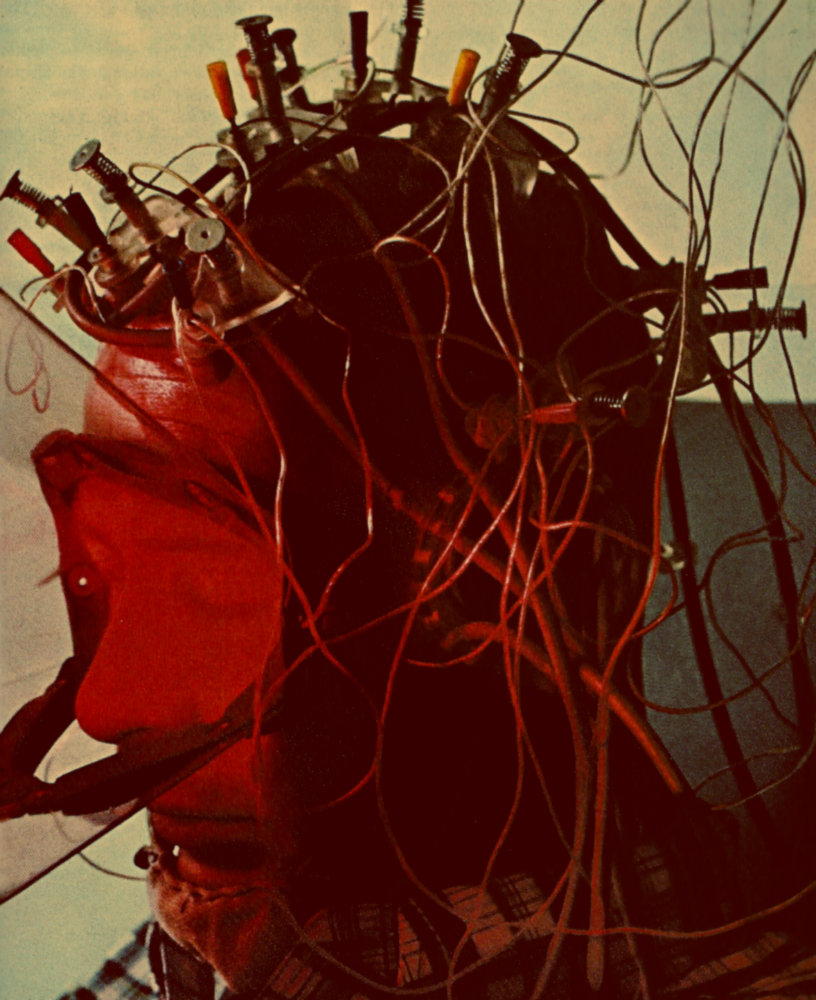
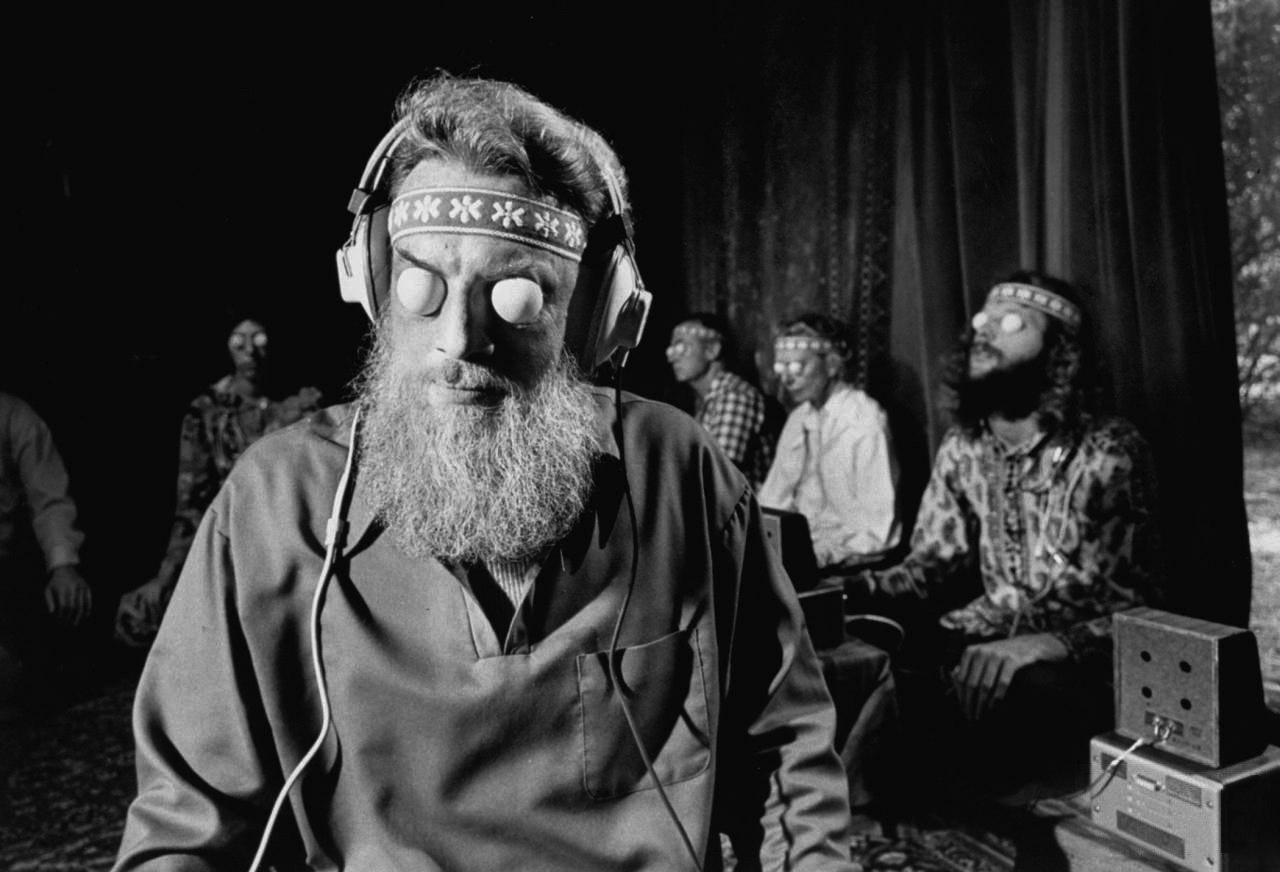
Universities around the globe and the U.S. government are trying to map the human brains, the tools to do so now a reality. But before such a mission was possible, people still wanted inside their heads, using whatever methods were at hand, even if they were deeply silly.
The article, “Flow Gently, Sweet Alpha,” published in a 1972 issue of Life, is a participatory journalism piece by Jane Howard about the biofeedback craze of the time. Howard travels to several locales–New York, Los Angeles and Laredo, Texas–having electrodes glued to her head, learning to “program her dreams,” taking imaginary excursions through cubes of metal and enrolling in a “Mind Control” course in search of enlightenment. Being hooked up to a biofeedback machine for 45 minutes cost $145 at the time. Jack Gariss, one of the L.A. spiritual gurus featured in the article, had an earlier career as a screenwriter, earning a credit for Cecile B. DeMille’s biblical blockbuster The Ten Commandments. An excerpt from the piece:
Mind Control does not use hardware. ‘Those machines are hopelessly obsolete already,’ one instructor told the 50 or so of us in my class. ‘We’re light years ahead of them. In these four days we’ll open up a channel that will make you feel like you can walk on water. You’d better start with puddles, though, until you’re used to being at your alpha level.’
The Silva Mind Control Institute of Laredo, Texas, was founded a year ago by a visionary electronics technician. ‘None of what you’ll learn here is new,’ our instructor told us in the New York City branch. ‘But José Silva is the first man in history to arrange these ideas in their proper sequence. It took him 26 years’ research.’
Mind Control has 50,000 graduates in 50 states and three foreign countries. In four days we would be graduates, too. We would learn all sorts of things. But first we had to stand up, one by one, and say what our zodiacal signs were, what we did for a living, and why we had come.
“I’m a Gemini and a barber, and I heard this course was really far out.”
“I’m a Serpico and a stockbroker, and I figured all this alpha stuff might give me insights about the market.”
“I’m a waitress, Pisces with Capricorn rising, and I’ll try anything once.”
“I’m a salesman and I don’t know anything about horoscopes, but my boss made me come.”
“I’m a Virgo and a ski instructor, and my mother gave me this course as a Christmas present.”
I said I was a Taurus (moon in Gemini) who wanted to learn to concentrate and relax.
“Close your eyes and take a deep breath,” our instructor would tell us during our conditionings. “Envision and repeat to yourself the number 5 three times.” Then 4 three times, and so on down to one. At one, he told us we were “entering a deeper, healthier level of mind, much deeper than before.”
Was this apha? Whatever it was, it felt good. At “my level,” I felt the way accomplished meditators claim to–as if a tidal wave were rushing through my forehead, sliding downward toward the spine, making leisurely spiraling loops along the way. Maybe I wasn’t walking on water, but I did feel more serene.
Phantasmagoric imagery appeared on what I was told was my “mental screen.” I saw coral reefs, mountain cabins, hotel rooms I’d occupied a decade ago, and the pattern on a painted cigarette box my mother had when I was a child. I heard a music box we’d had then, too. It was far more beguiling than a movie, finding all this richness lodged in my mind. I truly felt free of my usual trains of thought, so well trodden as seem almost paved.
But José Silva had not labored for nearly three decades just so we could see pretty pictures. Each conditioning had its topic and purpose. We were told how to sleep soundly, awaken refreshed, relax at will, and project healing energy onto our ailing friends from afar–not firsthand , because the laws about practicing medicine without a license.
We were told we could cancel out everything negative, but merely uttering the simple incantation “cancel, cancel.”•
I don’t give a screw about Star Trek, the TV series or films, but creator Gene Roddenberry was obviously a special guy and not only for his progressive outlook on race and gender. In a 1976 Penthouse interview conducted by Linda Merinoff, Roddenberry laid out the next 40 years of our society, from the Internet to email to swarms and crowdsourcing to the decline of the traditional postal service to online learning to the telecommunications revolution. Some of his longer-term thoughts on the natural evolution of humans were disquieting even to him. Three excerpts follow.
Penthouse:
What is happening to television as a piece of mechanical equipment?
Gene Roddenberry:
I think there is little doubt that we’re probably on the threshold of a whole new revolution in telecommunications. We are now experimenting with mating television sets with print-out devices, think of TV mated with a Xerox-type machine in which probably our newspapers will ultimately be delivered. It’s a much more efficient system. The minute you put the newspaper to bed electronically, you can then push a button and any house that subscribes to the service can have the thing rolled right out of the TV set. We’re also experimenting, in some cities already, with mating television with simple computers and the home will be run by a home-computing feature. You’ll do your billing on it, your banking, probably a great part of your shopping. I think it is inescapable that we mate TV with reproducing devices, that it will become our postal system of the future, almost certainly our telephone or videophone. So I see television going in either of two directions. One is that it can become that opiate we fear. Or, used properly, it can be a way for all people, everywhere, to have access to all the recorded knowledge of all humanity.
Penthouse:
Where do you think mankind is heading?
Gene Roddenberry:
There’s a theory I have that I’ve been making notes on for a couple of years now and intend to write a book on it sometime in the future. You often hear the question, “I wonder what the next dominant species will be?” I think that completely unnoticed by practically all people is the fact that the next dominant species on earth has already arrived and has been with us for some time. And this is a species that I call socio-organism. It first began to make its appearance when men started to gather together in tribal groups, and then city-states, and more lately in nations, giant corporations, and so on. The socio-organism is a living organism that is made up of individual cells–which are human beings. In other words the United States of America is a socio-organism. It is made up of 200 million cells, many of them become increasingly specialized just as the cells in our body do. Furnish food, take away waste products, or the nerves–the sight, the thinking, the planning. Your local PTA is also a small socio-organism. General Motors and ITT are socio-organisms. The interesting thing about this new creature is that unlike all the past life forms, one cell in a socio-organism can be a member of several of these socio-organisms. Also, they do not have to live in physical proximity with each other as in our bodies. It sounds a rather foolish sci-fi thing to say that General Motors is a living organism. But if you take a few steps back and view it from this point of view, you begin to discover that the evolution of this socio-organism almost exactly parallels everything we know about Darwinian evolution.
Briefly, Darwinian evolution is fairly generally accepted, that the first life forms on earth were individual cells floating on the warm soup seas of the time. Finally, through chance and other factors, groups of these cells discovered that by being gathered together they could get their food more efficiently, protect themselves, and become dominant over the single-cell amoebas. With humans, exactly the same thing happened. More and more individual units began to get more and more specialized. As it became more complex, with more and more highly specialized units, the creature became more and more powerful, was capable of protecting itself, taking care of its individual cells. This is a process of accumulating interdependence. The frightening thing about viewing humankind now, this way, is that the socio-organisms are really becoming more dominant than the individual. In Red China they are teaching the very lessons that our bodies have, over the centuries, taught to its cells–that we can no longer exist for ourselves. We must exist for the whole. But you can see the same thing in the United States. People now live the corporate morality. If I join a corporation, my duty is to the corporation. If the corporation says lie, cheat, steal, move here, do that, I must do it because my duty is to the whole. So if indeed civilization is following the laws of Darwinian evolution, you can predict ahead a few centuries or a few dozen or hundred centuries, until a time in which the independent individual will have totally vanished and this planet will be inhabited by totally specialized cells who function as part of these giant, living things. The great battle and great decision we humans face is whether to let this continue until we become faceless, totally interdependent organisms. Whether this is good or bad I don’t know. You might, if it were possible, talk to a cell of my heart and say, “Look cell, are you happy?” It seems to have adapted well. Maybe this is the way it suppose to be. Maybe there is some form of mass mind, mass consciousness, when a socio-organism reaches its final form, and we will be part of it and perfectly happy to be part of it. There may be contentments and happiness in this that we presently can’t visualize. I fear it because I can’t visualize it being better than remaining a free individual. I also fear the fact that if I remain, and insist on remaining totally independent and free, that the way things are going I am to be treated as a cancer cell by the socio-organisms around me, which will find it necessary to eradicate me because I endanger the organism.
Penthouse:
What is one’s purpose in this socio-organism? Just to survive?
Gene Roddenberry:
No. My purpose… that’s a hard question. I’ll try to answer it. My purpose is to live out whatever my function may be as a part of the whole that is God. I am a piece of Him. I believe that all intelligence is a part of the whole and it may be a great cyclical thing in which we have to go on, evolving, perfecting, until we reach the point where we are God, so that we can create ourselves so that we know we existed in the first place.
Penthouse:
You’ve said that you felt that Star Trek was a very optimistic show. Are you still that optimistic in the 70’s about the future of mankind?
Gene Roddenberry:
Yes, but I think that if we have an earth of the Star Trek century, it will not be an unbroken, steady rise to that kind of civilization. We’re in some very tough times. Our twentieth-century technological civilization has no guarantees that it is going to stay around for a long time. But I think man is really an incredible creature. We’ve had civilizations fall before and we build a somewhat better one on the ashes every time. And I’d never consider the society we depicted in Star Trek necessarily a direct, uninterrupted outgrowth of our present civilization, with its heavy emphasis on materialism. I think But my optimism is not for our society. It’s for our essential ingredient in humankind. And I think we humans will rebuild and, if necessary, we’ll lose another civilization and rebuild again on top of that until slowly, bit by bit, we’ll get there.•
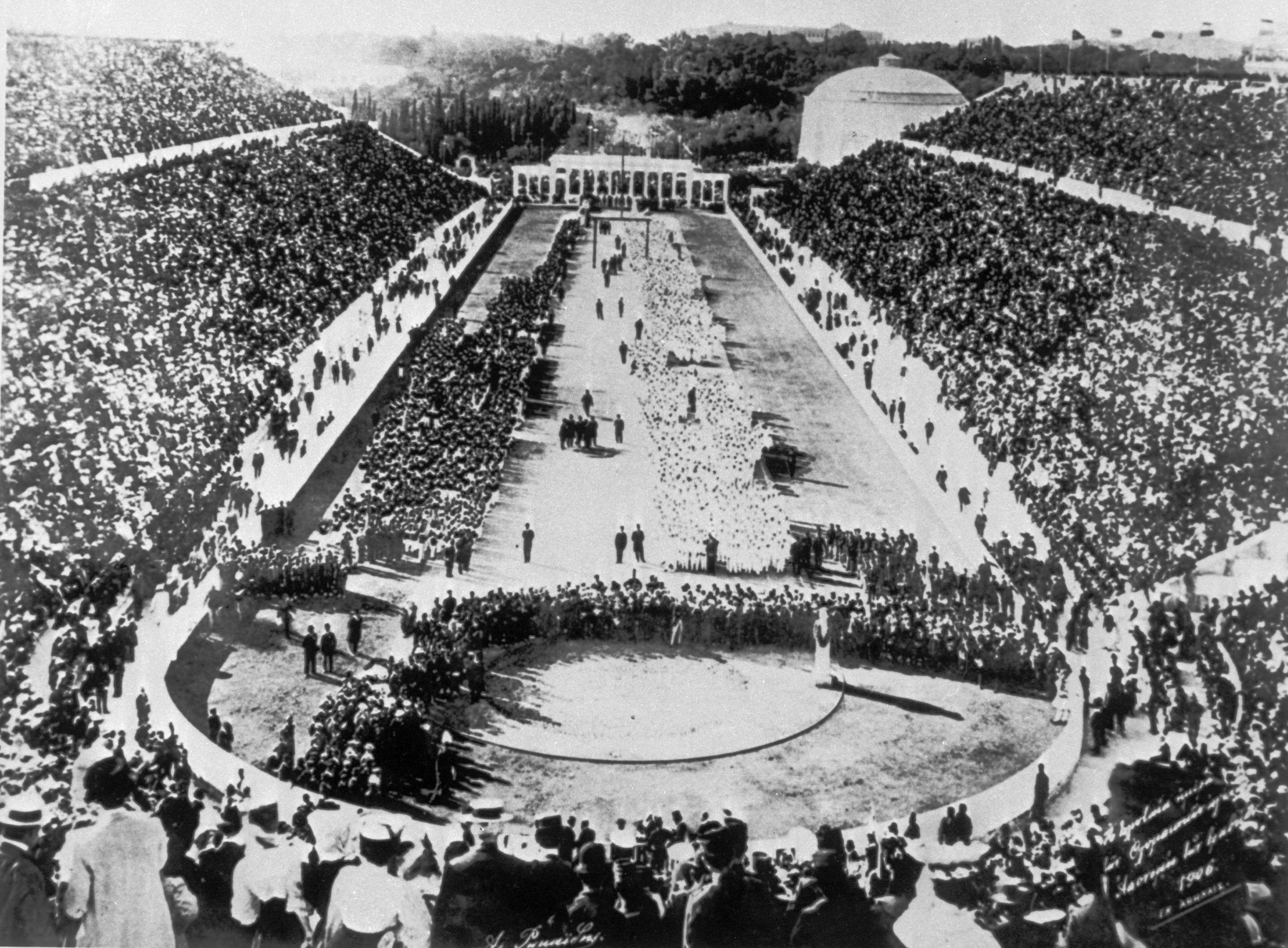
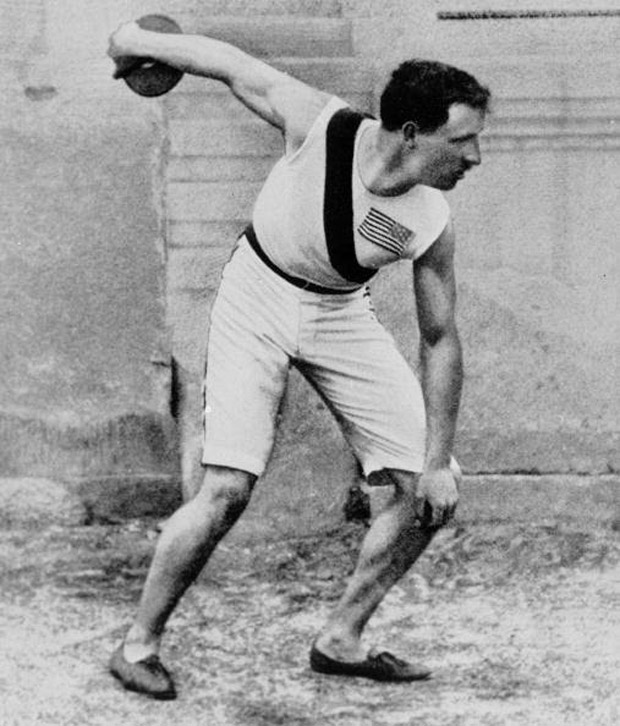
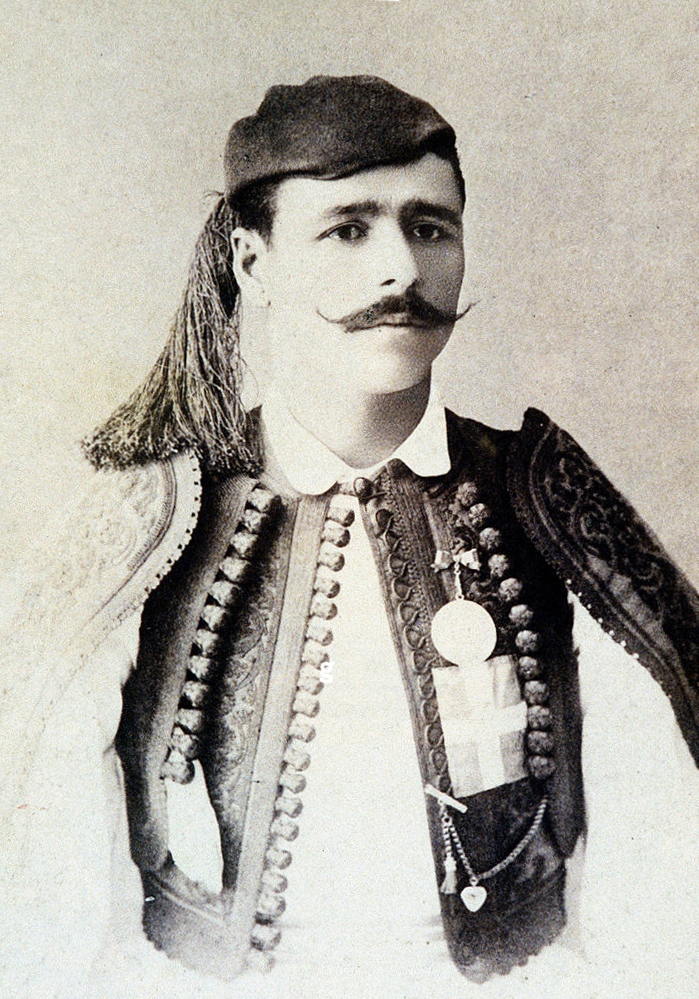
Today is the anniversary of the opening ceremony of the first modern Olympiad, the Athens Summer Games of 1896. While Greece would not host the event again for 108 years, this iteration was paramount for establishing a grandeur, truly globalizing the Games and instituting the Marathon as a major event. Photos above show Panathenaic Stadium, as well as competitors in field events, and unheralded Greek water-carrier Spyridon Louis, who won the Marathon. The particulars of latter event had a surprisingly academic source in French proto-semanticist Michel Bréal, who based its course on the legendary trek run by messenger Phidippides after the Battle of Marathon. Sadly, no women were allowed to participate due to the chauvinism of IOC founder Pierre de Coubertin, but one female still made a mark.
The Olympics sparked interest among American athletes in what had been largely unfamiliar activities, and later that year a collection of U.S. competitors convened in New York City to prepare for future Games. The chariot race was probably not necessary. From a report published in the September 6, 1896 Brooklyn Daily Eagle.
For the 2020 Summer Games in Tokyo, Japan is promising–perhaps overpromising–driverless taxis, robot assistants, instant language translation, etc. In the “et cetera” category is next-level maglev trains, which may reach a world-record 374 mph. Railroad geeks, a global phenomenon, are excited and turning out at viewing posts for test runs.
From Asahi Shimbun:
FUEFUKI, Yamanashi Prefecture–Railway buffs are getting up close and personal with the new superfast maglev train after two special observation platforms overlooking a test line were opened to the public last month.
In addition to seeing the ultimate in train technology speed past at close quarters, observers can also take in the beautiful backdrop of the expanse of the Kofu Basin and the peaks of the Southern Japan Alps.
As most parts of the test line has been carved underground through mountains, the observation platforms provide rare photo opportunities and places to wait for the test train.
The Yamanashi maglev test line is for what will be called the Linear Chuo Shinkansen, and when it goes into service it will allow passengers to travel between Tokyo and Nagoya in just 40 minutes.
One of the lookouts, the Hanatoriyama observatory, is in a park called “Linear no Mieru Oka” (hill where the linear motor train can be seen). The park spreads out over 2,900 square meters including the area for car parks for visitors.•
During the 1930s, a surprising number of American captains of industry looked longingly at Mussolini’s Italy and even Hitler’s Germany. What they thought they saw was indomitable power. How can we compete with well-coordinated Fascism and totalitarianism, they churlishly asked, with our impudent U.S. laborers? They’ll eat our lunch.
Although Mussolini met with the business end of a meat hook and Hitler died a bunker-based suicide, modern China has aroused those feelings of jealousy all over again in some of our current pouty plutocrats. There is some cause for envy. It’s awe-inspiring what that nation has done in short order, with its headlong dive through the Industrial Age and into the Digital one. Tens of millions have been lifted from abject poverty through mass, manic urbanization, though the day-to-day costs have been steep. It’s striking, though, that while the world’s highest cancer rates and the planet’s worst air pollution receive plenty of attention, the new money has seemingly papered over how sick the larger system is. Authoritarianism is still antithetical to human nature.
Xi Jinping’s current tough-on-crime crusade, aided by cutting-edge sensors and algorithms, is more a political purge than a righteous reckoning for the corrupt. It’s Mao married to modern technology.
The opening of “Crackdown in China,” Orville Schell’s excellent NYRB article:
“As a liberal, I no longer feel I have a future in China,” a prominent Chinese think tank head in the process of moving abroad recently lamented in private. Such refrains are all too familiar these days as educated Chinese professionals express growing alarm over their country’s future. Indeed, not since the 1970s when Mao still reigned and the Cultural Revolution still raged has the Chinese leadership been so possessed by Maoist nostalgia and Leninist-style leadership.
As different leaders have come and gone, China specialists overseas have become accustomed to reading Chinese Communist Party (CCP) tea leaves as oscillating cycles of political “relaxation” and “tightening.” China has long been a one-party Leninist state with extensive censorship and perhaps the largest secret police establishment in the world. But what has been happening lately in Beijing under the leadership of Chinese Communist Party General Secretary Xi Jinping is no such simple fluctuation. It is a fundamental shift in ideological and organizational direction that is beginning to influence both China’s reform agenda and its foreign relations.
At the center of this retrograde trend is Xi’s enormously ambitious initiative to purge the Chinese Communist Party of what he calls “tigers and flies,” namely corrupt officials and businessmen both high and low. Since it began in 2012, the campaign has already netted more than 160 “tigers” whose rank is above or equivalent to that of the deputy provincial or deputy ministerial level, and more than 1,400 “flies,” all lower-level officials.1 But it has also morphed from an anticorruption drive into a broader neo-Maoist-style mass purge aimed at political rivals and others with differing ideological or political views.
To carry out this mass movement, the Party has mobilized its unique and extensive network of surveillance, security, and secret police in ways that have affected many areas of Chinese life.•
Tags: Orville Schell, Xi Jinping
From the December 28, 1921 New York Times:
Pittsburgh, Pa.–The nimble Pirates, minus the tendency to crack in the heat of a National League pennant chase, and a Pitt football team that will display more agility than any trick movie star, are promised for 1922 by A. Lincoln Bowden, a Pittsburgh oil man, who has volunteered to supply both aggregations with dried monkey meat during the coming year. Glands will be included in the menu, according to the Pittsburgher, who has offered his services in the spirit of a devoted gridiron and diamond fan and says he wants Pittsburgh athletes to beat the world.
Mr. Bowden is about to depart for South America to lay in a supply of monkeys of a superior class, which he has frequently observed in Ecuador. The invigorating element of monkey meat and glands, he asserted, will give indomitable power and unlimited aggressiveness to the baseball and football men.
In proof of his assertions, he points to the case of of a Pittsburgher who was in Ecuador with him two months ago. In this case, Mr. Bowden said, although the patient was quite bald, a diet of monkey meat caused new hair to grow on his head, while all pains and aches left him and neither the heat of the jungle nor the cold of high mountain plateaus affected him in the slightest degree.•