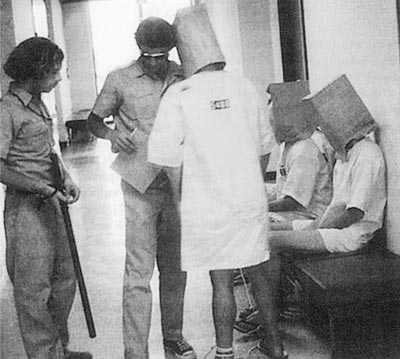
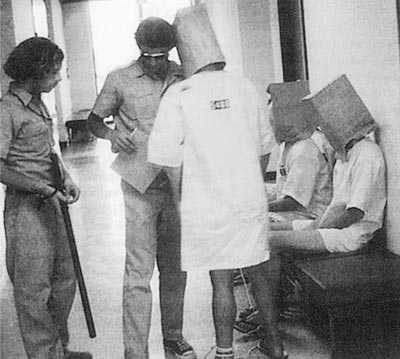
Philip Zimbardo, the head warden of the 1971 Stanford Prison Experiment, a dress rehearsal of sorts for Abu Ghraib, has misgivings about his most infamous research, which featured 18 college-aged male students playing jailers and inmates in a scene that rapidly deteriorated, acknowledging mistakes were made. He still would do it all over again, however.
While the cruel exercise reminded us that humans, under just the right (or, more accurately, wrong) circumstances, can forget their decency, a species that needed to receive that memo just 26 years after the fall of Nazi Germany may be too plagued by a short-term memory to survive its worst instincts.
In his more recent incarnation, Zimbardo has argued that technology is diminishing males, making guys receptacles for “porn, video games and Ritalin.” Sounds dubious. I don’t know that the geeks at Comic-Con are really what mainly ails us.
I suppose two examples, even such outsize ones, don’t equal a trend, but it would seem Zimbardo is very distrustful of young males, consistently believing them ready foot soldiers for one sort of evil or another. There’s some truth there, but it’s usually their elders who truly drive large-scale violence, conjuring up the sordid scenarios.
In a Salon Q&A conducted by Chauncey DeVega, Zimbardo considers the danger of America’s resting bitch face, Donald Trump, a Simon Cowell-ish strongman who would undo democracy itself if permitted. The psychologist makes a lot of good points, though his rationale for maintaining that he would still go forward with the SPE if he had it to do all over again is positively Trump-ish: “It’s the most widely known experiment in psychological history,” he points out in defense.
An excerpt:
Question:
You are perhaps most well known for the Stanford Prison Experiment. In hindsight, how do you feel about it?
Philip Zimbardo:
It’s the most widely known experiment in psychological history. I would do it again. Only I would not play the role of superintendent because in that role you get sucked into it. It was me and two students working around the clock. The prison is breaking down every day. There are parents visiting, parole board hearings, police and prison chaplains coming. There’s escape rumors. It was overwhelming. I know I could not have gone another week.
Question:
What lessons do you think the Stanford Prison Experiment holds for American society at present?
Philip Zimbardo:
What was dramatic about the study was the rapidity and ease with which intelligent college students who were otherwise normal and healthy followed their roles as prisoners and guards. We gave them no clue of what it means to be a guard. You know, in our culture prison guards are people who have power over prisoners who have less power — except that prisoners have the power of numbers. Guards have to convince prisoners that even though there are fewer of them, they have the weapons; they have other means of power to suppress them. You make them feel helpless and ineffectual.
Question:
What scares you right now? What gives you hope?
Philip Zimbardo:
Despite all the Trumpism, I’m optimistic about human nature that right will prevail over wrong. Heroism will prevail over evil. For me, again as an educator, it’s really important that teachers have to be anti-Trump in their own political mentality, their own morality. Whether or not they can present those political views in class, they can certainly prevent the Trump political views from being espoused. When kids act Trump-like, they can stop it cold. They can stop Trump-like bullying. They could call it for what it is.
I’m optimistic that Trump and his ideals will go away and people will laugh about it in the near future while saying, How could we have been so stupid?•